27382 Calle Arroyo, San Juan Capistrano, CA, 92675
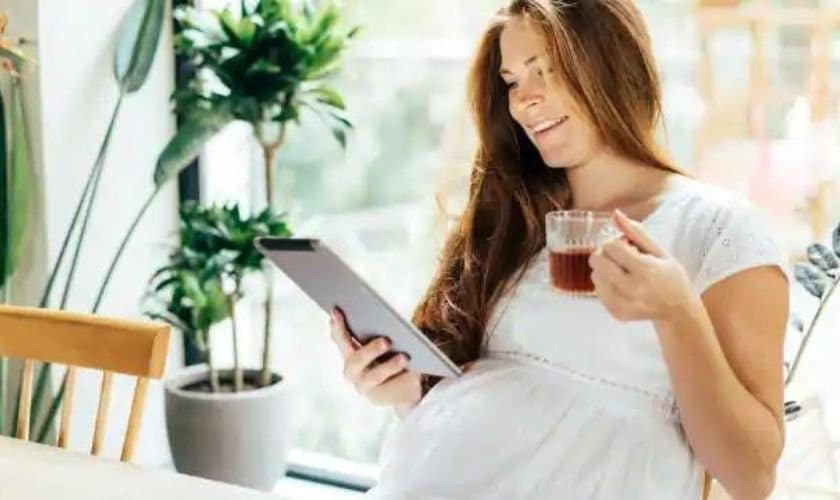

Fluoride is one of the most widely used additives in dental hygiene products today. It is used to reduce dental decay, help prevent cavities, and even strengthen enamel. However, some studies have raised concerns about whether or not fluoride intake during pregnancy can harm a baby’s development. While more research is needed to fully understand the risks of excessive fluoride intake during this period, it is essential for expecting mothers to be aware of the potential dangers and make educated decisions about their dental care routine.
Benefits of Fluoride During Pregnancy
Reduces Dental Decay
Fluoride helps strengthen tooth enamel and reduces the risk of dental decay resulting from acids produced by bacteria in plaque. It makes it an essential addition to dental health routines, as dental problems can be particularly difficult to manage during pregnancy.
Prevents Cavities
By strengthening tooth enamel, fluoride helps prevent cavities from forming. It is vital for pregnant women, as dental issues can affect their overall health and the health of their unborn babies.
Relieves Pain and Discomfort
Cavities that are not treated quickly can cause pain and discomfort. Fluoride helps protect teeth from developing cavities so that dental problems can be dealt with before they become painful and uncomfortable.
Risks of Excessive Fluoride Intake During Pregnancy
Possible Links to Fetal Brain Damage
Some studies have suggested that excessive fluoride intake during pregnancy may be linked to fetal brain damage. It is an area that requires further research to determine whether or not there is a real risk associated with fluoride intake during pregnancy.
Increased Risk of Lower IQ Scores
Some studies have suggested that excessive fluoride intake during pregnancy may increase children’s risk of lower IQ scores. Again, more research is needed to understand the potential risks associated with fluoride consumption during this period.
Potential for Negative Effects on Bone Development
Excessive fluoride intake may also lead to adverse effects on bone development in unborn babies. While this has yet to be proven through conclusive evidence, it is something that all expecting mothers should consider when making dental health decisions.
The Final Thought
At this point, the research on fluoride intake during pregnancy is inconclusive, and more research is needed to understand its potential risks entirely. However, it is essential for expecting mothers to be aware of the possible adverse effects that excessive fluoride consumption may have on their unborn baby’s development. To ensure dental health during pregnancy, it is recommended that pregnant women follow a preventive dental care routine and limit their exposure to dental hygiene products containing fluoride.
1. Is it safe to use dental hygiene products containing fluoride while pregnant?
While some studies suggest that excessive fluoride intake may be linked to fetal brain damage, there is not enough evidence to prove this definitively. Therefore, it is best to follow a preventive dental care routine and limit exposure to dental hygiene products containing fluoride while pregnant.
2. Can dental problems during pregnancy affect my unborn baby’s health?
Dental problems can directly impact an expecting mother’s overall health and the health of her unborn child. It is important for expecting mothers to pay attention to dental health issues and seek treatment if necessary to protect their and their babies’ well-being.
3. Does fluoride intake during pregnancy increase the risk of lower IQ scores in children?
Some studies suggest that excessive intake of fluoride may be linked to lower IQ scores in children, but more research is needed to understand this potential risk fully. Therefore, it is important for expecting mothers to follow dental health routines and limit their exposure to dental hygiene products containing fluoride during pregnancy.