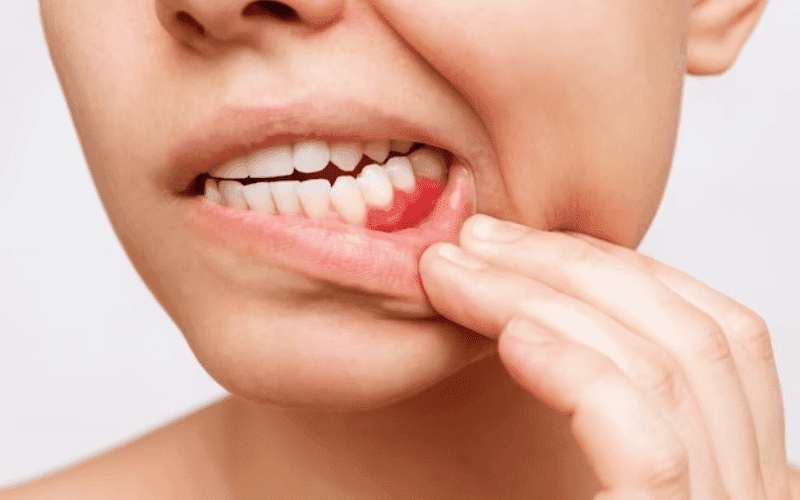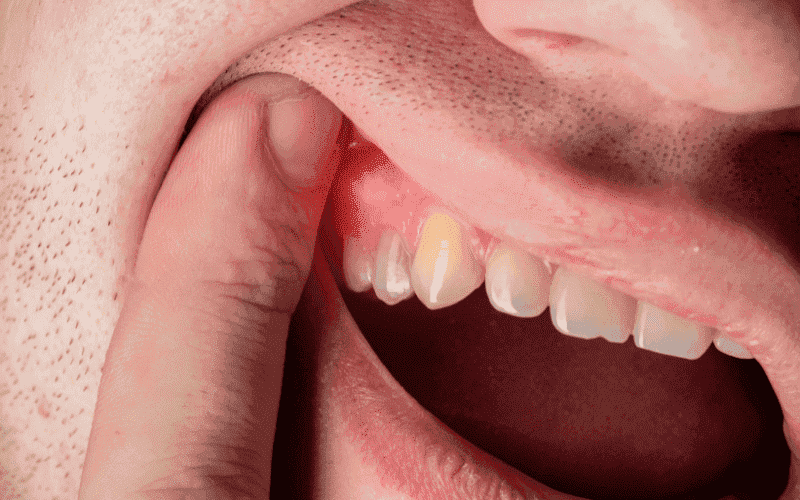
Keeping your mouth healthy isn’t just about a pretty smile. It’s crucial for overall well-being. Periodontal disease, a gum infection, is a major threat. If left unchecked, it inflames and weakens the gum tissue and bone supporting your teeth. This gradual breakdown can lead to teeth loosening and eventually falling out.
Early signs like swollen gums or bleeding during brushing might seem minor, but they signal the need for dental attention. Taking care of your gums through good oral hygiene and regular dental visits is vital to prevent tooth loss and keep your mouth healthy.
Understanding Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease is a common dental condition caused by bacterial infection affecting the gums and surrounding tissues. It starts with gingivitis, marked by swollen, bleeding gums, and progresses to periodontitis, where deeper gum pockets form, leading to bone and tooth loss. Poor oral hygiene, smoking, genetics, and certain diseases increase risk.
Treatment includes professional cleaning, antibiotics, and, in severe cases, surgery to restore gum health. Prevention involves regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, which are crucial for maintaining oral health and preventing complications like tooth loss and systemic health issues linked to periodontal disease.
Causes
Here are the five main causes of periodontal disease:
1. Poor oral hygiene: This is the most significant cause of periodontal disease. If you do not brush and floss your teeth regularly, plaque (a sticky film of bacteria) can accumulate on your teeth. Plaque irritates the gums and can eventually lead to infection.
2. Smoking: Smoking weakens the body’s immune system, making it harder to fight off infection. It can also irritate the gums and make it more difficult for them to heal.
3. Diabetes: Diabetes can make it harder for the body to control blood sugar levels. High blood sugar levels can create an environment in the mouth that is more hospitable to bacteria.
4. Genetics: Some people are more genetically predisposed to gum disease than others.
5. Hormonal changes: Hormonal changes, such as those during pregnancy, puberty, and menopause, can also increase the risk of gum disease.
Stages of periodontal disease
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is an infection that damages the soft tissue and bone that support your teeth. It’s a common problem that can lead to tooth loss if left untreated. Periodontal disease progresses through two stages: gingivitis and periodontitis.
1. Gingivitis: It is the earliest stage of gum disease. It is caused by plaque buildup, a sticky bacterial film that forms on your teeth. Gingivitis is reversible with good oral hygiene, such as brushing and flossing your teeth regularly. Symptoms of gingivitis can include:
– Red, swollen, or tender gums
– Gums that bleed easily while brushing or flossing
– Bad breath
2. Periodontitis: It is considered a more serious stage of gum disease. It occurs when gingivitis is left untreated. In periodontitis, the inflammation spreads to the bone and connective tissues that support your teeth. This can damage the bone and cause your teeth to loosen or even fall out. Symptoms of periodontitis can include:
– All the symptoms of gingivitis
– Pus between your teeth and gums
– Loose teeth
– Deep pockets between your teeth and gums
– A receding gumline (the gums pull away from your teeth)
– Changes in how your teeth fit together.
Periodontitis is also classified by severity. Here’s a breakdown of the stages:
1. Early periodontitis: Slight bone loss is evident on x-rays.
2. Moderate periodontitis: More bone loss is evident on X-rays, and pockets between the teeth and gums may be more profound.
3. Severe periodontitis: Significant bone loss is evident on x-rays, and teeth may become loose.
4. Advanced periodontitis: Severe bone loss is evident on x-rays, and teeth may become so loose that they fall out.
The Link Between Periodontal Disease and Tooth Loss
Periodontal disease, stemming from bacterial infection of gums and tissues, is a leading cause of tooth loss. It begins with gingivitis, marked by swollen, bleeding gums, and progresses to periodontitis, which damages the bone-supporting teeth. Bacteria release toxins, triggering inflammation and weakening tooth support.
As gum pockets deepen, teeth lose stability and may eventually fall out or require extraction. Poor oral hygiene, smoking, genetics, and systemic diseases exacerbate risk.
Early detection and treatment through professional cleaning, antibiotics, and surgical interventions can prevent tooth loss. Maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups are key to preserving teeth and gum health.
Can Periodontal Disease Lead to Tooth Loss?
Yes, periodontal disease can lead to tooth loss. It starts with gingivitis, causing swollen, bleeding gums, and progresses to periodontitis, where bacterial infection damages the gums and bone supporting the teeth. As the disease advances, pockets form between the gums and teeth, weakening their foundation.
Bacteria release toxins, triggering inflammation and further bone loss, eventually causing teeth to become loose and potentially fall out. Factors like poor oral hygiene, smoking, genetics, and systemic diseases increase susceptibility.
Early detection and treatment with professional cleaning, antibiotics, and surgery can prevent tooth loss, emphasizing the importance of oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups.
Tips for Preventing tooth loss from periodontal disease
Here are 5 tips to prevent tooth loss from periodontal disease:
1. Brushing and Flossing Regularly: Brushing your teeth twice a day and flossing once daily is the cornerstone of good oral hygiene and helps remove plaque and bacteria that can build up at the gum line and lead to periodontal disease.
2. Regular Dental Visits: Schedule regular dental checkups and cleanings every 6 months. This allows your dentist to detect and treat gum disease in its early stages before it can progress and lead to tooth loss.
3. Maintain a Healthy Diet: Sugary and starchy foods can contribute to plaque buildup. Limit your sugary and processed foods intake, and focus on eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These foods provide the nutrients your body needs for good oral health.
4. Stop Smoking: Smoking weakens the immune system and makes it harder for the body to fight off gum infections. Apart from this, there are other side effects of smoking as well, that affect our oral health. Stopping smoking is one of the finest things you can do for your general health, which includes your dental health.
5. Manage Stress: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system and make you more susceptible to gum disease. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, relaxation techniques, or time in nature.
Wrap Up!
Understanding gum disease, a condition characterized by inflammation and infection of the gums, and its correlation with tooth loss is paramount for maintaining a vibrant smile and optimal overall health. Delaying action can exacerbate the issue, leading to irreversible damage.
Recognizing the warning signs, such as bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, and gum recession. Take proactive steps by scheduling your Periodontal Care in San Juan with Ortega Cottage Dentistry, where our experienced team is dedicated to preserving your natural teeth for a lifetime of confident smiles. Don’t hesitate to contact us today to prioritize your oral health and well-being.